HORMONAL COIL (IUS)
WHEN and HOW?
When can a Hormonal Coil be inserted?
A hormonal coil (IUS) can be inserted into your uterus at any time of your cycle as long as you are not pregnant.
Please note the following:
- If the hormonal coil is inserted during the first 7 days of your cycle, you are immediately protected from pregnancy.
- If it is inserted at any other time of your cycle, you must use additional contraception, such as condoms, for 7 days.
The hormonal coil (IUS) is highly effective – the efficacy is 99% with typical use.
How is the Hormonal Coil (IUS) placed?
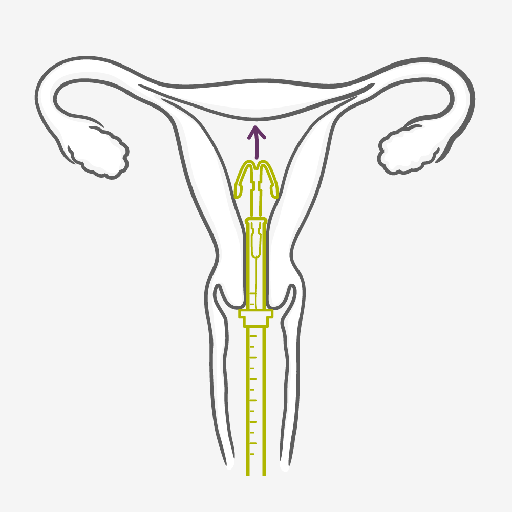
- Before the IUS is inserted, your doctor will check the position and size of your uterus.
- You may also be tested for existing infections, such as STIs, and receive antibiotics.
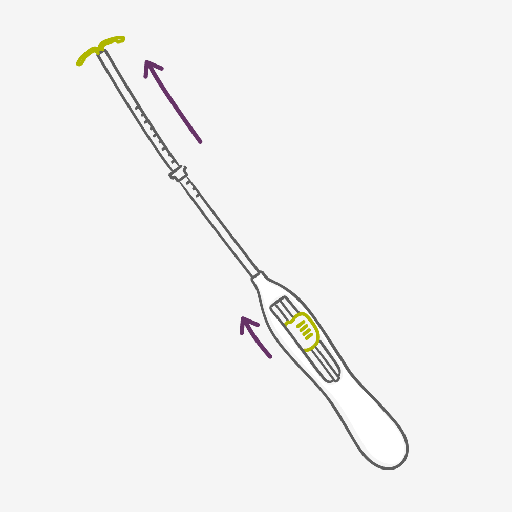
- Your healthcare provider will use an inserter to fit the hormonal coil into your womb. This can be uncomfortable or painful, but you can have a local anesthetic to help. Ask for pain medication (this can be given before or also after the insertion) or local anesthesia.
- If you experience pain or discomfort during the insertion of the hormonal coil, please inform your healthcare provider. You can stop it at any time.
- After the IUS has been inserted, a follow-up appointment is often scheduled to make sure everything is fine. It's important that you keep this appointment.
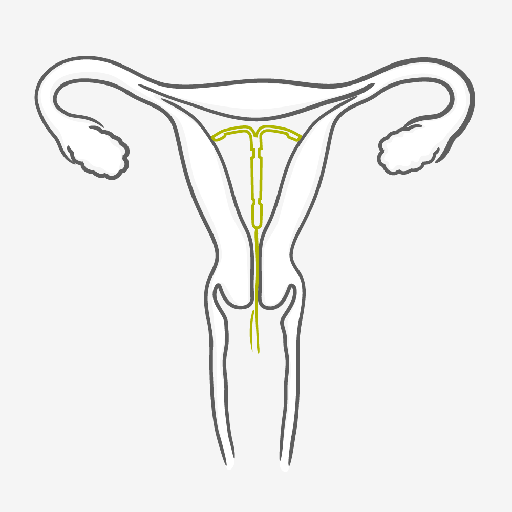
Once the IUS has been fitted by a well-trained healthcare provider, you’re highly protected from pregnancy from 3 to up to 8 years, depending on the type. Slight period-type cramps may occur afterwards. In case of any concerns please talk to your doctor.
IUS WHEN and HOW?
When can an IUS be inserted?
An IUS can be inserted into your uterus at any time of your cycle as long as you are not pregnant. Please note the following:
- If the IUS is inserted during the first 7 days of your cycle, you are immediately protected from pregnancy.
- If it is inserted at any other time of your cycle, you must use additional contraception, such as condoms, for 7 days.
How is the IUS placed?
- Before the IUS is inserted, your doctor will check the position and size of your uterus.
- You may also be tested for existing infections, such as STIs, and receive antibiotics.
- Your healthcare provider will use an inserter to fit the IUS into your womb.
This can be uncomfortable or painful, but you can have a local anesthetic to help. Please discuss this with your doctor in advance.
- Ask for pain medication (this can be given before or also after the insertion) or local anesthesia.
- If you experience pain or discomfort during the insertion of the IUS, please inform your healthcare provider. You can stop it at any time.
- After the IUS has been inserted, a follow-up appointment is often scheduled to make sure everything is fine. It's important that you keep this appointment.
Once the IUS has been fitted by a well-trained healthcare provider, you’re highly protected from pregnancy for up to 3 or 5 years, depending on the type.
Slight period-type cramps may occur afterwards. In case of any concerns please talk to your doctor.
Tabs header
HORMONAL COIL (IUS) PROS:
- It can stay in place for either 3 or 8 years (depending on the type), but can be removed any time.
- At 99.8%, it’s one of the most effective contraceptive methods
- It doesn’t interrupt sex
- Heavy periods can become lighter and less painful
- Some women may have shorter lighter or less frequent periods, which reduces the chances of becoming anemic
- Suitable for women who want long-acting reversible contraception for up to 3 or 8 years and wish to avoid daily, weekly or monthly regimens
- It can be used when breastfeeding
- Fertility returns to its previous level once the hormonal coil (IUS) is removed
HORMONAL COIL (IUS) CONS:
- It requires a trained healthcare provider for insertion and removal
- Irregular bleeding and spotting can be common in the first 6 months of use
- Some women experience headaches, tenderness and acne after an IUS is fitted
- It may cause cramps and/or irregular bleeding
- Small risk of infection at insertion and of expulsion
- Does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- It is rare but the IUS can come through the wall of the womb when it is put in (fewer than 2 in 1000)
- Pregnancy outside the womb (ectopic pregnancy) is possible but very rare.