CERVICAL CAP
WHEN and HOW?
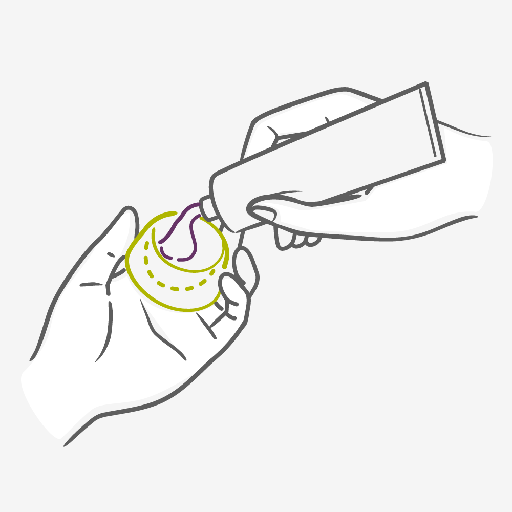
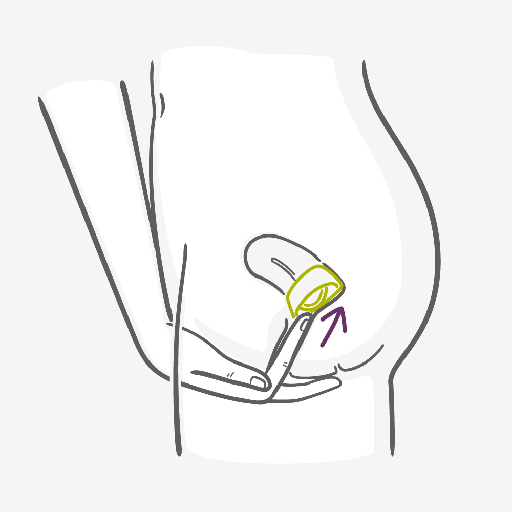
You must put the cap in the vagina before you have sex and this might feel a little tricky at first but practice, as always, makes you more familiar with the process. The cervical cap has an efficacy of 84% with typical use.
How to use the cervical cap?
The cap should not be used alone though, to keep yourself properly protected the cap should always be used with spermicides.
The cervical cap comes in different size, ranging from 22 to 26 mm. A pelvic examination by your doctor or healthcare provider will determine which size you need based on your obstetrical history. Get more information here
Tabs header
CERVICAL CAP PROS:
- It can be used on demand
- They are easily carried with you
- It isn’t affected by other medications
- It can be used when breastfeeding
- Hormone free
- Low cost
CERVICAL CAP CONS:
- It can interfere with sexual spontaneity
- Using it can take practice
- It requires keeping track of the hours inserted
- Not always suitable for women who have given birth
- Requires initial fitting by healthcare provider
- Effectiveness increases when used in combination with spermicides
- Low efficacy even when used as directed
- The cap may cause irritation or allergic reactions
- If you keep it in place longer than 48 hours, there is a risk of toxic shock syndrome. Toxic shock is a rare but serious infection
- Does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)