THE CONTRACEPTIVE PILL
WHEN and HOW?
The pill is taken every day in most cases. But there are different types of regimen:
- 21 day regimen (21 days 1 pill every day followed by 7 days of no pill)
- 28 day regimen (21 days of pills with hormones followed by 7 days of hormone-free pills)
- 24/4 regimen (24 days of pills with hormones followed by 4 days of hormone-free pills)
The contraceptive pill has an efficacy of 93% with typical use.
How to use the contraceptive pill?
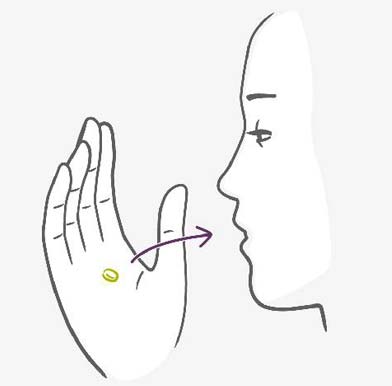
Taking the pill is the same as taking other tablets, you put one in your mouth and swallow it. You should swallow the pill at the same time every day, whether you have sex or not. As described above, there are different types of pills and the best way to find out exactly how to use them, is to read the Patient Information Booklet provided to you with the pill pack or to ask your doctor.
Forgetting to take your pill means it won’t be as effective as it can be and you could find yourself getting pregnant. If you miss 1 or more pills, or start a pill pack too late, have a look into the Patient Information Booklet provided to you with the pill pack. In case of doubt, or if you experience any side effects, please talk to your healthcare provider.
You can also use our Forgot the pill tool to get more advice.

Tabs header
Contraceptive Pill PROS:
- Highly effective when used as directed
- It permits sexual spontaneity and doesn’t interrupt sex
- Some pills may reduce heavy and painful periods
- Some pills may have a positive effect on acne
- Can be taken over a long period of time
- Easy to use
- Easy to hide
Contraceptive Pill CONS:
- Does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- It requires keeping track of the number of days taken
- Some women experience mood swings, depression, or depressed mood
- Some women experience breast tenderness, nausea, headache, weight gain
- It may cause changes in your menstruation cycle
- It is not common, but some women who take the pill develop high blood pressure
- It is rare, but some women will have blood clots, heart attacks and strokes
All important details about the Contraceptive Pill
There are a few different types of contraceptive pills:
- The combined pill contains estrogen and progestin, which stop the ovaries from releasing eggs. It also thickens the cervical mucus, which keeps the sperm from getting to the egg.
- The so-called mini pill contains only one hormone, a progestin, which offers an alternative to those affected by the hormone estrogen.

Questions & Answers about the Pill
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
No, there are many different types of contraceptive pills available, and each of them is slightly different. The important thing is to follow the instructions that come with your pill package exactly. It’s important to take the pills as directed because missing pills or taking them not on time make them less effective. If you have any questions about how to take the pill, ask your healthcare provider for further advice.
Hormones used in the pill are mostly a synthetic form of the natural hormones progestin and estrogen. Some contain only a progestin, e.g. progestin-only pill, others a combination of progestin and estrogen, e.g. the so-called combined pill.
The combined pill mimics a pregnancy to your body, although you are not pregnant, what prevents you from ovulation. It also thickens the mucus in the cervix, which makes it difficult for sperm to get through.
The progestin only pill works by thickening the mucus at the entrance to the womb. In some women it may also prevent ovulation.
Some contraceptive pills can improve the condition of your skin and hair; others help with symptoms such as acne, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), and irregular menstrual bleeding.
The pill is one of the most reliable forms of contraception, giving a very high degree of protection against pregnancy when taken as directed.
No it is not necessary to take a 'pill break' unless you want to get pregnant. There is no effect on long-term fertility even if you take hormonal contraceptives for years.